1. Overall Health Benefits of Tesofensine
Tesofensine offers a range of potential benefits, including promoting weight loss, improving cognitive health, enhancing mood, regulating blood sugar levels, boosting energy, addressing sexual dysfunction, treating eating disorders, managing ADHD, improving sleep quality, and aiding in the fight against alcohol addiction.
- Promotes weight loss [6-23]
- Improves cognitive health [24-32]
- Improves mood [33-35]
- Improves blood sugar levels [36-38]
- Increases energy levels [35, 39]
- Treats sexual dysfunction [35, 40]
- Treats eating disorders [8, 41-45]
- Treats attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) [46-49]
- Improves sleep quality [50-57]
- Fights alcohol addiction [58-62]
2. Key Takeaways of Tesofensine Guide 2023
- Tesofensine is a triple re-uptake inhibitor that increases the levels of three neurotransmitters in the brain: Serotonin, norepinephrine, and dopamine.
- Tesofensine benefits include weight loss, fat loss, increased energy levels, improved sex drive, better erections, improved mood, improved memory, improved concentration, better sleep, and better blood glucose levels by improving insulin sensitivity and glucose metabolism. Tesofensine causes a significant increase in weight loss and fat loss by reducing appetite, increasing resting energy expenditure (ie increasing metabolism and calories burned), increasing fat oxidation, and reducing fat tissue.
- Tesofensine is one of the most effective, powerful weight-loss medications available on the market. Studies have shown more weight loss with higher tesofensine doses was up to 1 mg. A clinical study found that participants receiving tesofensine at doses of 0.25 mg, 0.5 mg, and 1.0 mg in conjunction with a prescribed diet for 6 months had a mean weight loss of 4.5%, 9.2%, and 10.6%. Comparatively, patients in this study treated with a placebo only lost an average of 2% of their body weight. There was a 4-point drop in BMI in a period of 24 weeks in those treated with 0.5 mg and 1 mg.
- Tesofensine has been shown to have a good safety profile and was well tolerated although an increased number of adverse events (e.g., increased heart rate and blood pressure) were observed in the higher dose groups of 0.5 mg and 1.0 mg. Blood pressure and heart rate were increased by 1–3 mmHg and up to 8 bpm, respectively. Other side effects of Tesofensine may include dry mouth, headache, nausea, insomnia, diarrhea, and constipation. Although some studies show it may have anti-anxiety properties, some people may experience an increase in anxiety levels. Side effects are dose-dependent and are more significant when using higher doses.
- The tesofensine dosage range used in studies was 0.25 mg to 1 mg. The weight loss of 9.2% in the 0.5 mg tesofensine dose vs 10.6% in those using the 1 mg tesofensine dose may not justify the dose-dependent increases in side effects. Based on this, the best tesofensine dose for most patients would be 0.5 mg or lower. You should consult your weight loss expert doctor to determine if tesofensine is right for you and the dosage should be custom tailored.
- Only purchase tesofensine through a legally accredited US pharmacy prescribed by your expert weight loss doctor custom tailored for you. Do not buy tesofensine online because there are no testing requirements or regulations of these products to guarantee that it is even tesofensine, that is high-quality tesofensine, and that it is pure and does not contain any harmful chemicals. Consult with an expert weight loss doctor who has a lot of experience prescribing tesofensine and understands its potential side effects, contraindications, and drug interactions. A thorough medical history and exam should be completed along with the appropriate blood work. Caution: Tesofensine is a prescription medication that can cause side effects and it may not be a good weight loss option for you based on your medical history, blood work, or current medication use. An expert weight loss doctor will help you determine this. Tesofensine is not a supplement and should not be purchased online as a supplement. It is also very unwise for humans to use this medication by purchasing it online on websites that sell it with the legal loophole that it is being sold “for research purposes only”.
3. What is Tesofensine?
Tesofensine (NS2330) is a serotonin–noradrenaline–dopamine reuptake inhibitor or also known as a triple reuptake inhibitor, which means that it inhibits the reabsorption of the neurotransmitters (brain chemicals) serotonin, norepinephrine, and dopamine. This process increases the levels of these neurotransmitters. The therapeutic benefits of tesofensine are attributed to this effect because each of these neurotransmitters exerts an important function at different locations in the brain. Tesofensine peptide has been investigated in clinical trials for its use in medical weight loss.
4. How Does Tesofensine Work?
Tesofensine works by boosting the levels of brain chemicals (neurotransmitters) such as dopamine, norepinephrine, and serotonin. Dopamine is associated with the regulation of motor function, mood, motivation, reward, cognitive function, and reproductive behaviors. Norepinephrine increases the force of the contraction of the skeletal muscle and the heart to ensure optimal body function. Serotonin is responsible for the regulation of mood, memory, sleep, and appetite.
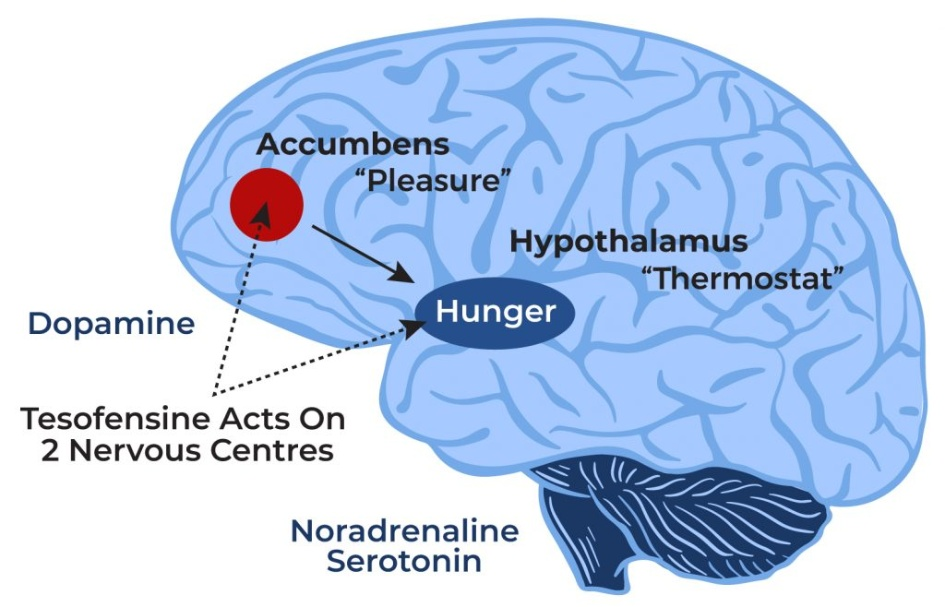
5. Chemical Structure of Tesofensine
6. Research Studies/Clinical Trials on Tesofensine
A. Promotes Weight Loss

Optimal dopamine levels have a positive impact on appetite regulation, metabolism, and motivation. On the other hand, dopamine deficiency can promote weight gain. Dopamine suppresses appetite, reduces cravings, and lowers calorie consumption. It also boosts metabolism by increasing thermogenesis, leading to improved calorie burning and increased energy expenditure. Moreover, dopamine enhances motivation and satisfaction, which helps produce feelings of satiety.
Tesofensine is widely known as a weight loss drug. Researchers believe that tesofensine may help treat obese and overweight patients because it boosts the levels of dopamine in the brain. A deficiency in this neurotransmitter has been shown to be linked with overeating and obesity. [1-5]
Fat oxidation, also known as lipid oxidation or fat burning, refers to the process by which stored fat is broken down and converted into usable energy within the body. There are some mechanisms by which tesofensine may contribute to increased fat burning such as increased metabolism, appetite suppression, and modulation of neurotransmitters. As an appetite suppressant, it may indirectly promote increased physical activity which leads to increased fat oxidation. When combined with lifestyle modification, the body responds well to the effects of tesofensine.
Discover the Power of Peptides for Weight Loss! Learn how peptides can support your weight loss journey and improve your overall health. Explore our comprehensive guide on peptides for weight loss at Genemedics and take the first step towards a healthier, happier you!
Clinical trials involving tesofensine have evaluated its efficacy and safety in promoting weight loss:
- The results of phase III trials such as the 2018 phase 3 Viking study showed that obese participants who received both doses of oral tesofensine (0.25 and 0.50 mg once daily) had statistically and clinically significant reductions in weight with low incidence of adverse events at week 24. [6]
- The results of clinical trials such as the Phase II b trial (TIPO-1) showed that obese patients lost an average of 12.8 kg on the 1 mg dose, 11.3 kg on the 0.5 mg dose, and 6.7 kg on the 0.25 mg dose of tesofensine (dose-dependent increase), and showed no statistically significant increases in systolic or diastolic blood pressure, compared with a 2.2 kg loss in the placebo group. [7] The 24-hour fat oxidation (fat burning) also increased by 15% and there was a reduction in protein oxidation (the breakdown of protein due to the presence of reactive oxygen species).
- In the TIPO-2 trial, tesofensine administration in obese individuals reduced their desire to eat and increased their satiety levels after 14 days of treatment. [8]
- In patients with obesity, tesofensine treatment at varying doses (0.25 mg, 0.5 mg, or 1.0 mg) resulted in statistically significant and clinically relevant weight reductions with positive effects on energy balance and appetite. The patients were also able to increase their physical activity gradually, which led to improved quality of life. Significant results were seen in the highest dose groups. [9]
- In obese participants, tesofensine administration at a dose of 0.5 mg for 26 weeks produced weight reductions twice that of anti-obesity agents such as sibutramine or rimonabant. [10]
- In overweight patients, tesofensine administration for 24 weeks is associated with enhanced appetite suppression and significant weight reductions. [11]
- In phase II clinical trials with tesofensine in obese individuals, significant reductions in weight, body fat, and waist circumference were observed without any adverse side effects. [12]
- In obese individuals, long-term tesofensine supplementation was well-tolerated and resulted in statistically significant and clinically relevant weight loss. [13]
- In patients with Parkinson’s or Alzheimer’s disease, tesofensine administration once daily for 14 weeks induced weight loss of approximately 4%, which is similar to that of sibutramine. [14]
- In healthy males, multiple administrations of tesofensine at doses of 0.125–1 mg resulted in the following positive results: increased dopamine levels and appetite suppression. [15]
- In diet-induced obese rats, tesofensine administration resulted in appetite suppression and weight loss with a reversal of low forebrain dopamine levels. [16-17]
- In a rat model of diet-induced obesity (DIO), administration of tesofensine (2.0 mg/kg, s.c.) for 16 days significantly reduced body weights. [18]
- In diet-induced obese rats, tesofensine treatment at 2 mg/kg for 28 days decreased food consumption and produced dramatic weight losses while preventing weight gain. [19]
- In 203 obese persons, tesofensine 0.5 mg produced a weight loss twice that of currently approved anti-obesity medications. [20]
- In obese participants, tesofensine administration resulted in a 10% average weight loss in 24 weeks. The patients were also able to increase their physical activity gradually after the treatment. [21]
- A study showed that tesofensine showed a more significant effect on body weight than that of currently approved anti-obesity drugs. [22]
- In obese patients, tesofensine in combination with an energy-restricted diet effectively reduced the weight of the subjects. [23]
B. Improves Cognitive Health

Research indicates that tesofensine helps preserve cognitive health by indirectly potentiating cholinergic neurotransmission, which is a process whereby nerve cells relay messages to each other. [24] This has been proven to have beneficial effects on various areas in the central nervous system and cognitive health including learning, memory, and thinking skills. This suggests that tesofensine may be used in the treatment of brain disorders such as Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s disease. The following studies support this effect:
- The first results of two small 4-week phase IIa clinical trials performed in patients with mild Alzheimer’s disease (AD) showed that tesofensine treatment induced significant improvement in cognitive function, indicating the need for phase III trials. [25-26]
- A growing body of research indicates that obesity is a major risk factor for cognitive impairment, especially in the older population. [27-30] With its anti-obesity effect, tesofensine may help protect against cognitive impairment.
- In a mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease, tesofensine administration decreased the brain concentrations of amyloid beta, which are abnormal protein aggregates and is the causative agent of the disease. [31]
- In patients with advanced Parkinson’s disease and motor fluctuations, low-dose tesofensine improved activities of daily living and motor function. [32]
C. Improves Mood

The mood centers of the central nervous system have also been shown to be positively affected by tesofensine. Sustained treatment with tesofensine has been shown to improve overall mood through its antidepressant effect. Studies show that tesofensine affects mood by:
- Increasing the levels of brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF), thereby triggering an antidepressant effect. [33]
- Triggering an anti-anxiety effect in obese individuals with comorbid depression and anxiety symptoms. [34]
- Increasing the levels of the neurotransmitters serotonin, noradrenaline, and dopamine. [35]
D. Improves Blood Sugar Levels
Tesofensine has also been found to have beneficial effects on blood sugar. By promoting weight loss, tesofensine may indirectly contribute to improving insulin sensitivity in individuals with obesity or overweight. Insulin sensitivity refers to the body’s ability to respond to the effects of insulin, a hormone that acts as a key to unlocking cells, thus allowing glucose (blood sugar) from the bloodstream to enter and be utilized by cells for energy production. Weight loss also plays a significant role in reducing blood sugar levels and decreasing the incidence of type II diabetes.
Clinical trials have shown that weight loss drugs such as tesofensine demonstrate efficacy in improving blood sugar levels:
- In obese patients, administration of tesofensine at varying doses (0.25 mg, 0.5 mg, and 1.0 mg) resulted in a reduction in blood sugar levels and improvement in quality of life with significant results observed in the highest dose groups. [36]
- In rodents, tesofensine also induced a significant reduction in blood sugar levels in addition to weight loss. [37-38]
E. Increases Energy Levels
Tesofensine treatment is also beneficial in improving one’s productivity by increasing energy levels. Medical weight loss programs with this medication can cause a significant increase in energy levels by having the following positive results: reduced appetite with balanced nutrition, increased physical activity, increased metabolism resulting in more calories being burned, and hormonal balance. Evidence supports the energy-boosting effects of tesofensine:
- A study found that tesofensine can boost energy by increasing the levels of the neurotransmitters dopamine and norepinephrine, which help regulate energy balance, motivation, interest, and drive. [35]
- The administration of tesofensine in overweight and moderately obese men induced higher energy expenditure compared to placebo. [39]
F. Treats Sexual Dysfunction

Because of its potent antidepressant effect, tesofensine has also been studied for its therapeutic benefits on sexual dysfunction, according to studies:
- Tesofensine has the capacity to increase the levels of dopamine, a neurotransmitter that contributes to the desire for sexual activity, erection, and ejaculation, making it beneficial for patients with sexual dysfunction related to dopamine deficiency. [35]
- Tesofensine administration is effective in treating depression-related sexual dysfunction, suggesting that it can help ramp up sexual power. [40]
G. Treats Eating Disorders

Studies reported that triple reuptake inhibitor such as tesofensine also holds therapeutic potential for eating disorders:
- In obese patients, tesofensine administration reduced their desire to eat and resulted in a significant increase in their satiety levels after 14 days of treatment without adverse events. [8]
- In patients with binge eating disorder, a condition in which a person eats large quantities of food when stressed, tesofensine administration has been shown to improve its symptoms, possibly due to tesofensine’s potent antidepressant effect, without an adverse event. [41-44]
- In the diet-induced obese rat, tesofensine induced appetite suppression by indirect stimulation of α1 adrenoceptor and dopamine d1 receptor pathways. [45]
H. Treats Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD)

ADHD is characterized by short attention span, hyperactivity, and impulsivity, and is common in children and even adults. Evidence suggests that tesofensine may have beneficial effects on this mental condition:
- Studies show that ADHD is strongly linked with low levels of dopamine and serotonin and that tesofensine can have beneficial effects on this condition by increasing the levels of these neurotransmitters. [46-48]
- A study reported that tesofensine can lower the risk of ADHD associated with obesity. [49]
I. Improves Sleep Quality

Studies suggest that tesofensine’s ability to increase the levels of certain neurotransmitters can help improve sleep quality:
- A deficiency in the neurotransmitter serotonin has been linked to insomnia and various sleeping difficulties. [50-55]
- Studies reported that increasing the levels of serotonin through selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor treatment has been shown to improve objective and subjective sleep quality in patients with sleeping difficulties – an effect similar to tesofensine. [56-57]
J. Fights Alcohol Addiction
Neurotransmitters play a significant role in alcohol addiction. Alcohol affects several neurotransmitter systems in the brain, leading to the addictive and rewarding effects associated with alcohol consumption. There’s also evidence suggesting that tesofensine can cure alcohol addiction via its ability to boost neurotransmitter levels:
- Studies show that low dopamine levels are associated with alcohol addiction – with tesofensine’s ability to increase dopamine levels, it may help reduce excessive alcohol intake along with its symptoms. [58-61]
- In ethanol-preferring rats, triple reuptake inhibitor administration reduced alcohol consumption without decreasing food or water consumption. [62]
7. Associated Side Effects of Tesofensine
Tesofensine side effects are very uncommon and similar to other currently approved diet pills and weight loss medications. There have been some side effects associated with the use of this drug wherein the patient had one of the issues listed below at some point while being on tesofensine. However, these side effects weren’t confirmed to be associated with the treatment and could have been a coincidence and not related to the use of tesofensine. Despite this, it was listed as a side effect associated with tesofensine even though these associated side effects are very uncommon.
Side effects associated with tesofensine may include the following:
- Constipation
- Diarrhea
- Dry mouth
- Headache
- Changes in blood pressure (increase blood pressure)
- Increased heart rate
- Insomnia
- Nausea
8. Tesofensine Dosage
Studies have indicated that the tesofensine dosage range employed was between 0.25 mg to 1 mg. However, the weight loss achieved with a 0.5 mg dose (9.2%) was only slightly lower than that of a 1 mg dose (10.6%). Considering the dose-dependent rise in side effects, it raises questions about the justifiability of higher doses.
Based on this information, for most patients, a tesofensine dose of 0.5 mg or lower appears to be the most suitable option. However, it is crucial to consult with your weight loss expert doctor to assess if tesofensine is appropriate for your specific circumstances and to determine the optimal dosage tailored to your needs.
The dosage of tesofensine is determined on an individual basis, taking into consideration various factors such as health conditions and medical history. It is important to note that not everyone may be eligible for tesofensine treatment due to specific health issues. Therefore, individuals are strongly advised to consult with a qualified tesofensine doctor or healthcare professional who has expertise in prescribing tesofensine. Seeking guidance from an expert will help ensure that tesofensine is prescribed in a safe and appropriate manner, tailored to the specific needs and circumstances of each individual.
9. Tesofensine vs Semaglutide
Tesofensine and semaglutide are both medications that have shown potential for weight loss in clinical trials, but they differ in their mechanisms of action and approved uses.
- Mechanisms of Action: Tesofensine is an inhibitor of pre-synaptic uptake of the neurotransmitters serotonin, noradrenaline, and dopamine. This causes appetite suppression and produces feelings of satiety. Semaglutide, on the other hand, is a glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) receptor agonist. It works by mimicking the action of a naturally occurring hormone called GLP-1, which helps regulate blood sugar levels and reduce appetite.
- Approved uses: Tesofensine is used for the treatment of obesity. On the other hand, semaglutide is an approved medication used for type 2 diabetes and obesity.
